What are Incoterms?

“What is Incoterms?
The abbreviation of the words (Incoterms), before you want to know what Incoterms 2020 is, it is necessary to say that the English word Incoterms means international commercial terms. In general, these terms are used to separate costs and responsibilities between the seller and the buyer. Incoterms is in fact a global term that oversees the transaction between the importer and the exporter. According to Incoterms rules, both parties must take responsibility for costs and responsibilities, as well as manage logistics and transportation from the product’s departure from the origin to its acceptance at the destination with their specific conditions. In order for Incoterms to cover new events in international trade and its changes, it is updated every period by the International Chamber of Commerce. Incoterms 2020 is considered the most up-to-date global version.”
مطمئناً، در اینجا ترجمه دقیق و کامل متن ارائه شده به انگلیسی آمده است:
Incoterms Terms and Types
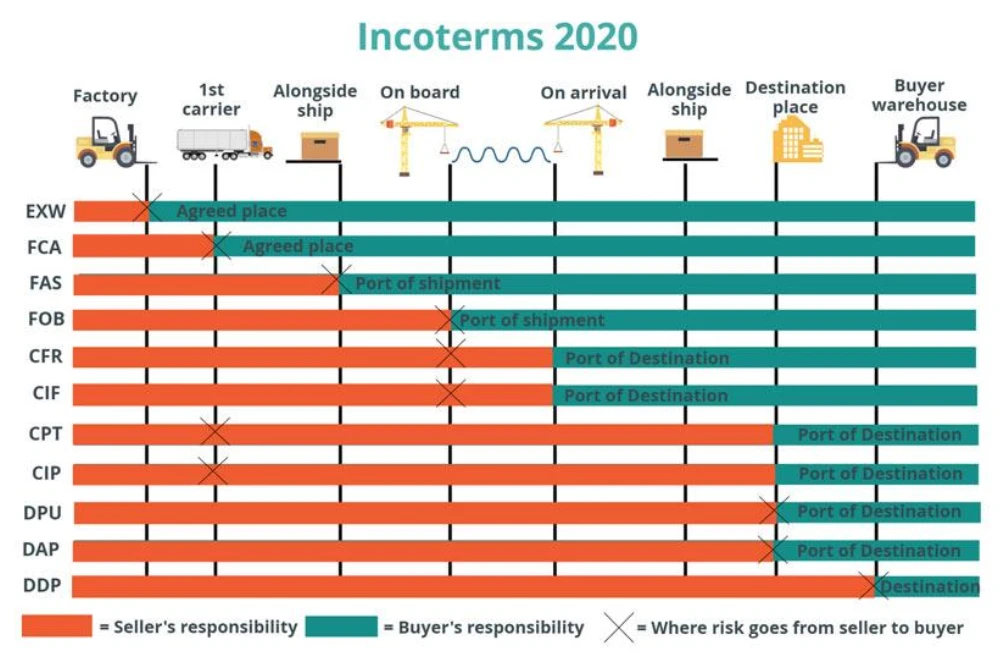
As mentioned, Incoterms include numerous trade terms used in transactions between sellers and buyers. These terms define the responsibilities and duties of both parties, as well as the conditions for paying freight costs. Using Incoterms terms in a transaction ensures clarity and transparency, with each party fully aware of their obligations. The main and basic Incoterms terms used in commercial transactions include:
- FCA (Free Carrier):
- The seller must deliver the goods to the carrier designated by the buyer at their premises or another specified location.
- The delivery location must be clearly specified, as all risks and responsibilities for the shipment transfer to the buyer.
- All shipping and insurance costs are the buyer’s responsibility.
- The seller has no obligation for import clearance, customs formalities, or import duties.
- CPT (Carriage Paid To):
- The seller must contract for and pay the freight to the named destination.
- The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller.
- This term is often used in multimodal transport (land or air).
- The seller’s risk ceases when the goods are delivered to the first carrier.
- The buyer is responsible for additional costs, including insurance and inspection.
- CFR (Cost and Freight):
- This term is used in sea freight.
- The seller must deliver the goods on board the ship and pay the freight.
- The seller’s responsibility ends once the goods are loaded on board the ship.
- The buyer is responsible for insurance and insurance costs.
- FOB (Free On Board):
- The seller must deliver the goods on board the ship at the port of shipment.
- The seller’s responsibility ends once the goods are on board the ship.
- All subsequent costs are the buyer’s responsibility.
- The buyer must also pay for shipping, insurance, and inspection.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight):
- This term is used in sea freight.
- The seller’s responsibilities end upon delivery and loading on board the ship.
- The seller is responsible for shipping, insurance, and freight costs.
Incoterms 2010 Sections
Incoterms 2010, the eighth version, defines transportation rules and terms. It consists of two main sections and eleven rules that detail buyer and seller responsibilities.
Section 1: Rules for Any Mode(s) of Transport
- EXW (Ex Works):
- The seller delivers the goods at their premises.
- The buyer is responsible for all subsequent costs and risks.
- FCA (Free Carrier):
- The seller delivers the goods to the carrier designated by the buyer.
- Buyer is responsible for main carriage.
- CPT (Carriage Paid To):
- Used in multimodal transport.
- The seller pays for freight to the named destination.
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To):
- The seller pays freight and insurance to the named destination.
- DAT (Delivered at Terminal):
- The seller pays for transportation to the terminal at the destination.
- Buyer pays for import duties.
- DAP (Delivered at Place):
- Used in any mode of transport.
- The seller delivers the goods at the named destination, buyer unload goods, and pay import duties.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid):
- The seller delivers the goods to the buyer’s country, paying all costs.
Section 2: Rules for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport
- FAS (Free Alongside Ship):
- The seller delivers the goods alongside the ship.
- Buyer pays for loading and main carriage.
- FOB (Free On Board):
- The seller delivers the goods on board the ship.
- Buyer pays for main carriage and insurance.
- CFR (Cost and Freight):
- The seller delivers the goods on board the ship and pays the freight.
- Buyer pays for insurance.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight):
- The seller delivers the goods on board the ship and pays freight and insurance.
Incoterms 2016 Terms
Incoterms 2016 is similar to Incoterms 2010, with some terms removed and others added. Common terms include:
- EXW, FCA, FAS, FOB, CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP, DDU, DDP
New terms in Incoterms 2016:
- DAF (Delivered At Frontier)
- DES (Delivered Ex Ship)
- DEQ (Delivered Ex Quay)
- DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid)
Incoterms 2020 Terms
Incoterms 2020 is the latest version, effective January 1, 2020, with changes to its rules and details. It includes the same eleven terms as Incoterms 2010 but with revisions.
Incoterms 2020 Changes
- Incoterms 2020 clarifies the risks, costs, and responsibilities of each party.
- DAT (Delivered at Terminal) is changed to DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded), allowing delivery at any location, not just terminals.
- Increased seller responsibility for insurance in CIP.
- Clarification on the responsibilities of the buyer and seller.
Incoterms 2020 vs. 2010 Differences
- DPU replaces DAT.
- Increased seller insurance responsibilities in CIP.
- Overall increased clarification of all rules.
